How to Get Started with Substance 3D Stager
Getting started with Substance 3D Stager might seem challenging, especially if you’re a beginner. However, by understanding the basics — system requirements, program installation, and the interface — you’ll be able to confidently move forward. Let’s break down the key steps.
System Requirements: Is Your Hardware Enough?
Before you begin, it’s important to ensure that your computer meets the program’s requirements. The graphics card plays a key role, especially if you’re working with high-poly models or complex materials.
If your computer is lagging, try optimizing the program’s settings or upgrading your hardware. For example, increasing RAM or using a more powerful graphics card can significantly improve performance.
Minimum requirements:
- Operating system: Windows 10 or macOS 10.15.
- Processor: Intel Core i5 or equivalent AMD.
- Graphics card: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1060 or higher.
- RAM: at least 8 GB (16 GB recommended).
Program Installation: It’s Simple If You Know the Nuances
Installing Substance 3D Stager is straightforward if you follow these simple steps:
- Download the installer from the official Adobe website.
2. Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions.
3. After installation, be sure to register in Creative Cloud to access all the program’s features.
Don’t forget to check for the latest updates after installation. This ensures you’re using the most stable version of the software.
Program Interface: What to Click and Where?
The Substance 3D Stager interface may seem complex at first glance, but it’s easy to master once you understand the main elements:
- On the left: the Objects panel, where you’ll find all added models.

- On the right: the Materials and Textures library.
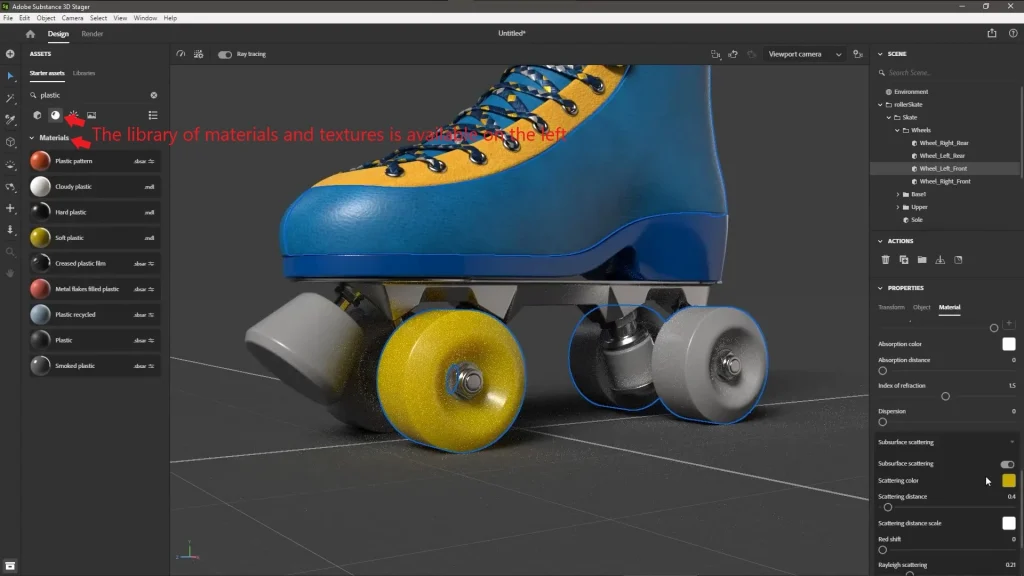
- In the center: the workspace, where you place and adjust objects.
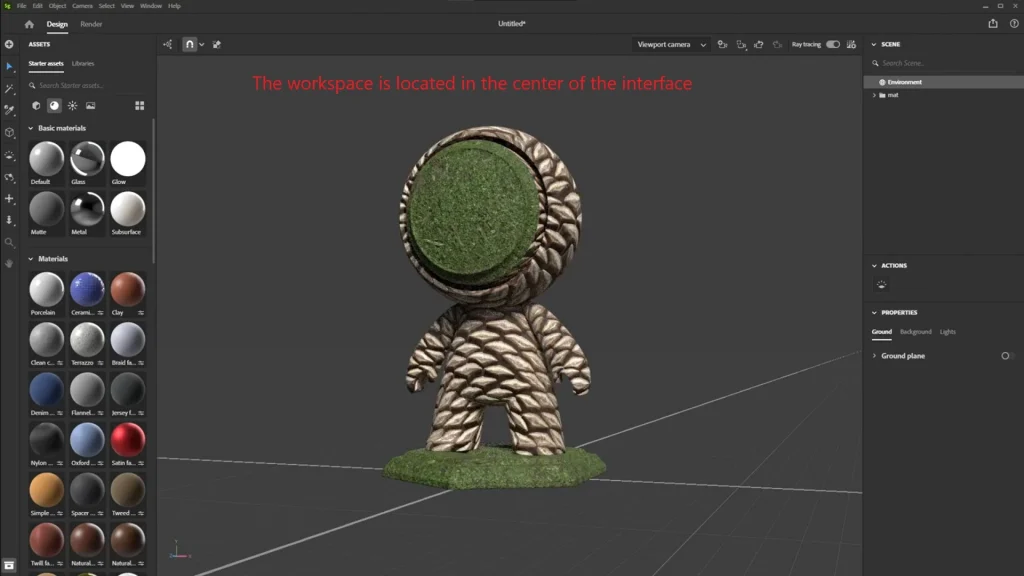
Spend some time exploring the interface to get comfortable. Try experimenting with simple objects to understand how they work.
How to Import and Place Objects in Substance 3D Stager
One of the key aspects of working in Substance 3D Stager is importing and placing objects. This is the foundation for creating realistic scenes, whether it’s product visualization, interiors, or game environments. Let’s break down this process step by step.
Importing 3D Models: Formats and Settings
The first step is to import 3D models into the program. Substance 3D Stager supports several popular formats:
OBJ: A simple and universal format suitable for most models.
FBX: Supports animation and complex materials, ideal for game assets.
GLTF/GLB: A modern format for web visualization with PBR material support.
Before importing, ensure that the model has a proper UV map and is optimized for use. Too high polygon density can slow down the program.
“I often use models from the Adobe Stock library because they are already optimized for Substance 3D Stager .”
Placing Objects: How to Achieve Harmony in the Scene
After importing, it’s important to properly place objects in the workspace. Here are a few tips:
- Use movement, rotation, and scaling tools: These tools are available at the top of the interface.
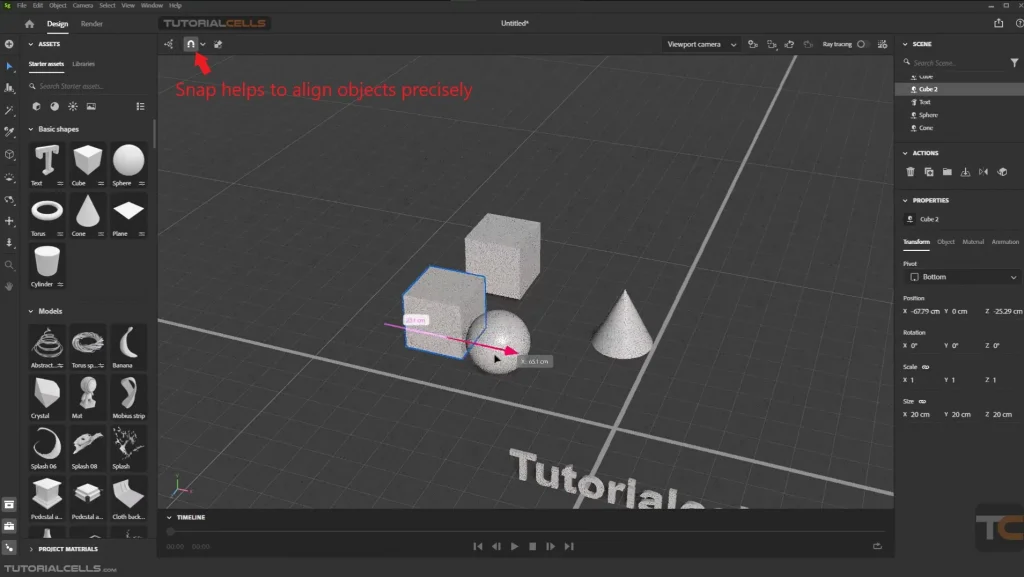
2. Snap: Enable snap to precisely align objects relative to each other or surfaces.
3. Group objects: If you’re working with multiple objects, group them for easier management.

“I often use snap to accurately place furniture in interior scenes.”
Adjusting Object Parameters
Each object can be customized for better integration into the scene:
- Transparency: Useful for creating glass or translucent materials.
- Reflection: Adjust metallic and roughness settings for realistic light reflection.
- Height: Add relief to the object using height maps.
Experiment with object parameters to achieve the desired effect. For example, increase roughness for wood or decrease it for metal.
How to Adjust Materials and Textures in Substance 3D Stager
Adjusting materials and textures is one of the most important steps in working with Substance 3D Stager , directly impacting the realism of your scene. Let’s explore how to apply ready-made materials, create custom textures, and adjust their parameters to achieve the desired effect.
Applying Materials: How to Make Objects Realistic
Substance 3D Stager has an extensive library of ready-made materials that you can use for your objects. Here’s how it works:
- Select the object in the workspace.
- Find a material in the library on the right and drag it onto the object.
- Adjust material parameters such as roughness, metallic, and transparency.
Use HDRI maps to create a realistic environment. This will help materials look more natural.
“I often apply a wood material from the Adobe library to quickly create a realistic table.”
Creating Custom Materials
If the ready-made materials aren’t enough, you can create your own textures. Use integration with Substance 3D Designer or other tools:
- Create a texture in Substance 3D Designer (e.g., a noise pattern for stone).

2. Import the texture into Substance 3D Stager .
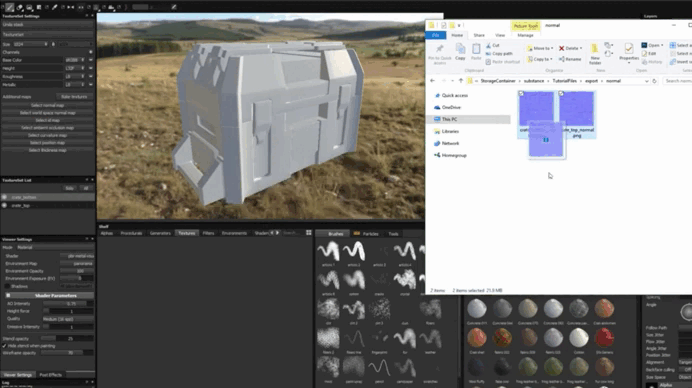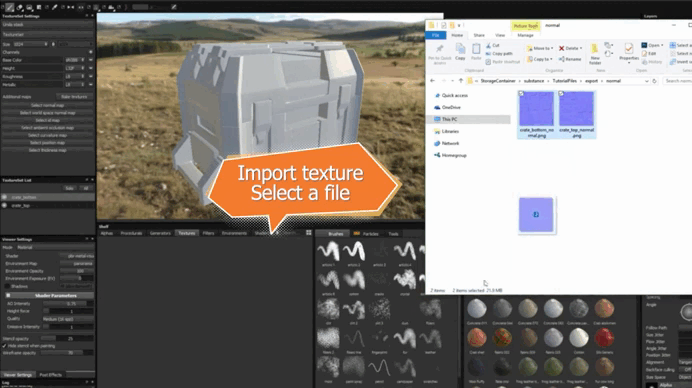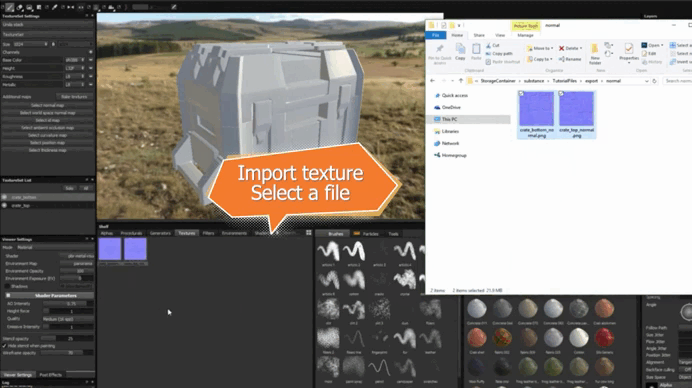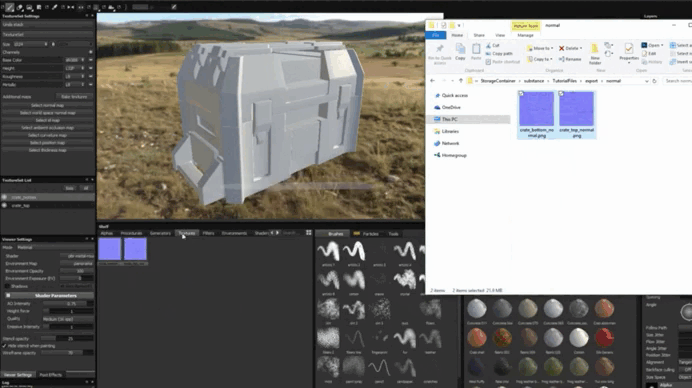
3. Apply the texture to the object and adjust its parameters.
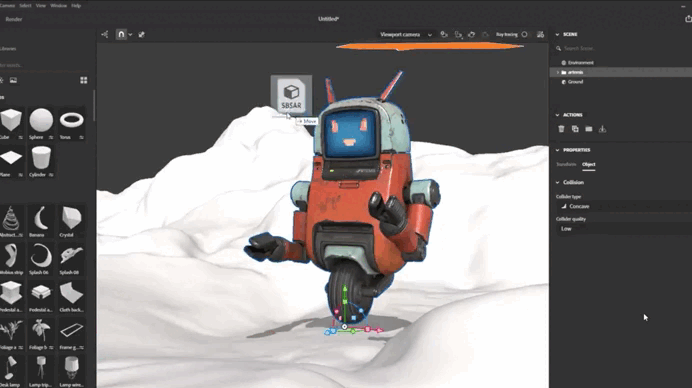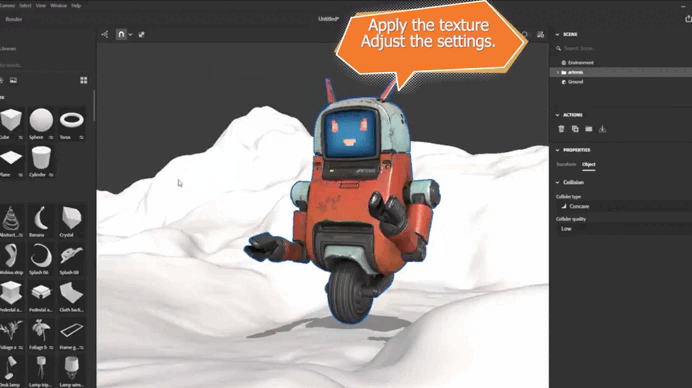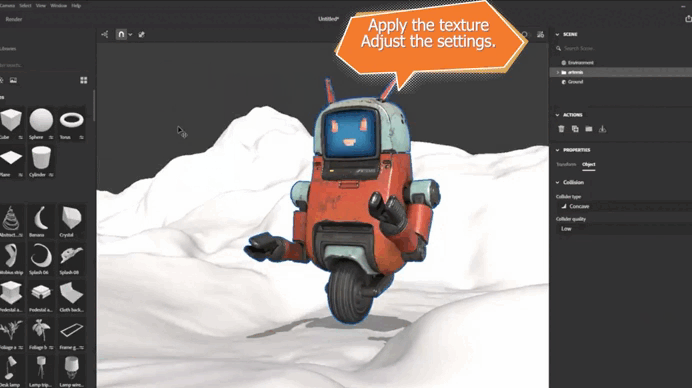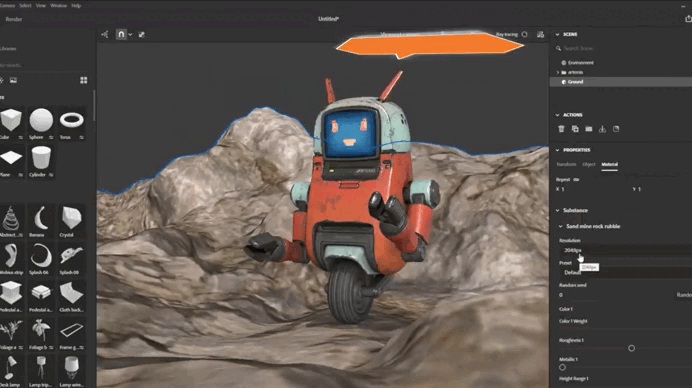
“I combine several noise nodes in Designer to create a complex rust texture and then import it into Stager.”
Adjusting PBR Materials
PBR (Physically Based Rendering) is the standard for creating realistic materials. Here are the main parameters to adjust:
- Roughness: Determines how much the surface reflects light.
- Metallic: Indicates whether the material is metal.
- Height: Adds relief to the texture.
Experiment with parameters to achieve a natural effect. For example, a surface that’s too glossy might look artificial if it’s supposed to be matte.
How to Set Up Lighting and Cameras for Realistic Visualization
Lighting and cameras are two key elements that determine how realistic your scene will look. Let’s explore how to properly adjust these parameters in Substance 3D Stager to achieve professional results.
Setting Up Lighting: Secrets to Realism
Lighting plays a crucial role in creating the atmosphere of a scene. Here are some tips for setting it up:
- Adding Light Sources:
Use directional light (Directional Light) to create shadows.
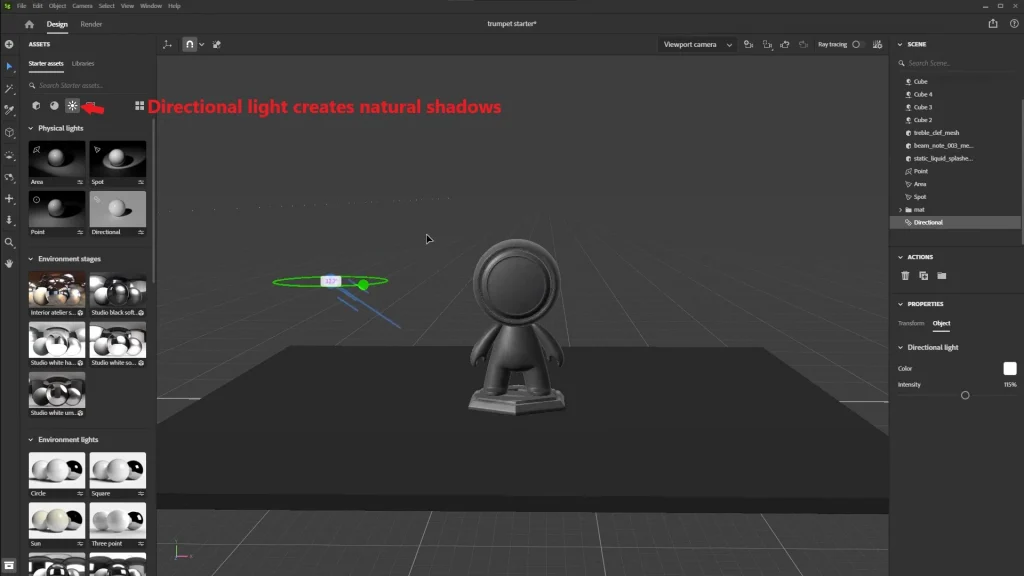
Point lights (Point Light) help highlight specific objects.
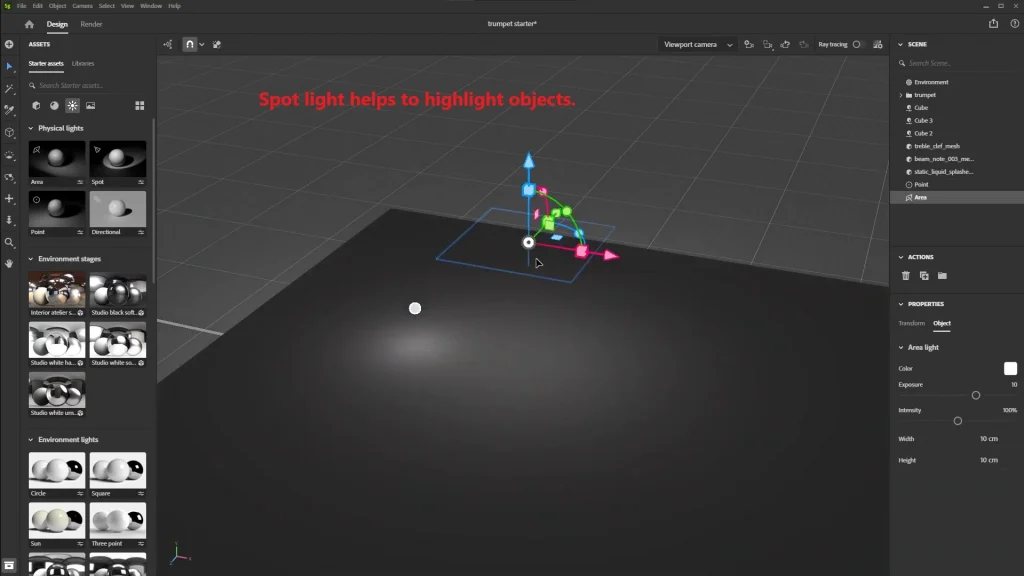
Spotlights (Spotlight) are ideal for focused lighting.
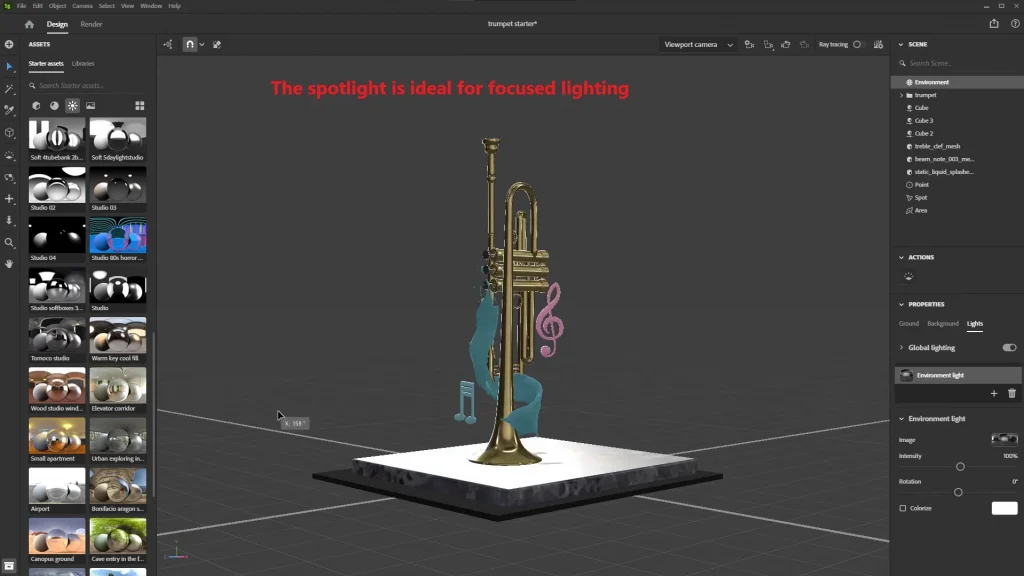
- Using HDRI Maps:
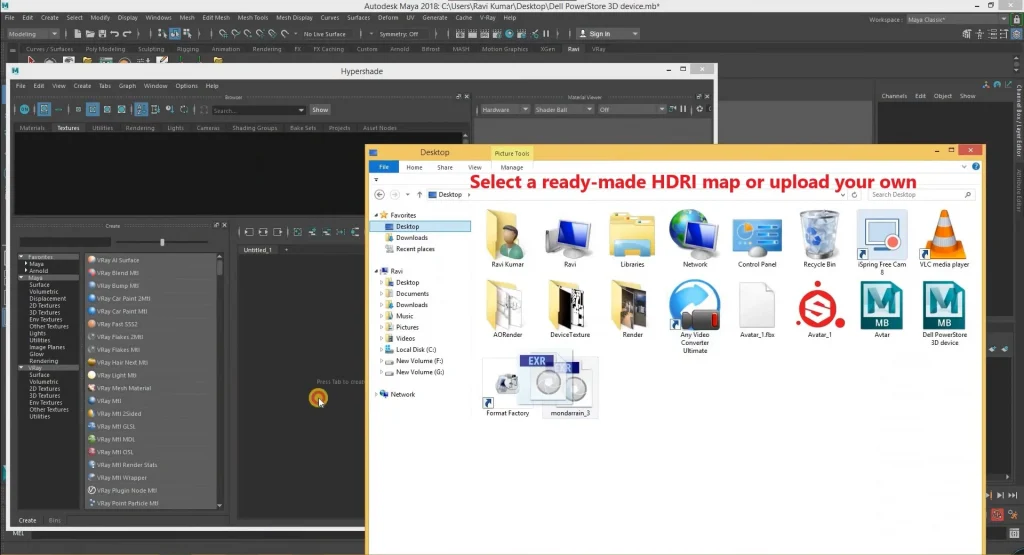
HDRI maps create a realistic environment by simulating natural lighting.

You can choose a ready-made map from the library or upload your own.
If you want soft lighting, choose HDRI maps with diffused light. For dramatic effects, use maps with strong contrasts.
“I often use an HDRI map with a sunset to add warmth to the scene.”
Setting Up Cameras: How to Get the Perfect Angle
Cameras allow you to control how your scene will look in the final visualization. Here are the main settings:
- Camera Position: Place the camera so it captures all important objects.
Use the rotation tool to find the best angle. - Focal Length: Short focal length (e.g., 24 mm) creates a wide field of view.
Long focal length (e.g., 85 mm) is suitable for portrait scenes. - Depth of Field:
Enable depth of field to blur the background and focus attention on the object.
“I often use a focal length of 50 mm to achieve a natural perception of the scene.”
How to Export Scenes and Use Them in Other Programs
After creating a scene in Substance 3D Stager , it’s important to export it correctly for further use. Let’s explore the key aspects of this process: export formats, integration with other programs, and quality checks.
Export Formats: Which One to Choose?
The choice of export format depends on your goals and the program you’re using. Here are the main formats to consider:
- PNG/JPG: Suitable for high-quality static images.
- FBX/GLTF: Ideal for exporting 3D models with textures and animations.
- TGA/EXR: High-quality formats for professional work.
If you’re working in Unreal Engine or Unity , choose the FBX format — it’s the most supported and ensures flexibility in adjustments.
It’s also important to configure export settings:
- Make sure all materials and textures are exported along with the model.
- Check the texture resolution: for games, values typically range from 1024×1024 to 4096×4096 pixels.
Integration with Unity and Unreal Engine
Importing scenes into Unity or Unreal Engine is easier than it might seem. To do this:
- Drag and drop the model and texture files into the project.
- The program will automatically apply them to objects if the UV mapping is set up correctly.
In Unreal Engine , materials can be configured through the Material Editor. For example, you can combine different maps (normals, roughness, metallic) to create complex materials.
In Unity , the process is similar: simply assign the textures to a material, and they’ll appear on the model right away.
If the textures aren’t applied correctly, check whether the texture names meet the program’s requirements. For example, in Unreal Engine , normal maps often need to be named “NormalMap”.
Checking Scene Quality
Before exporting, always check your scene for issues. Here are a few tips:
- Ensure that textures aren’t stretched or distorted. This could be due to poor UV mapping.
- Check the lighting: it should look natural and align with your goals.
- Zoom in on the scene in a 3D editor to see fine details. For example, dirt or scratches should look realistic.
If you notice any problems, go back to Substance 3D Stager and adjust the scene. It’s better to spend a little more time checking than to fix errors later.
Useful Tips for Working Effectively in Substance 3D Stager
Working in Substance 3D Stager can seem challenging, especially if you’re just starting out. To simplify the process and avoid common mistakes, we’ve compiled a few helpful tips that will make you a more efficient user of the program.
Hotkeys: How to Speed Up Your Workflow
Hotkeys are your best friend in Substance 3D Stager . They significantly speed up your workflow and allow you to focus on creativity rather than searching for tools. Here are some combinations worth memorizing:
- Ctrl + Z: Undo the last action. It’s basic but extremely important.
- Space: Rotate the camera in viewing mode. This is handy when you need to inspect the scene from all angles.
- G: Switch between objects and materials.
- Shift + F: Quickly toggle between texture display modes (e.g., normals, roughness).
Write down a list of the most frequently used hotkeys and keep it near your workspace. Over time, they’ll become second nature.
Avoid Common Mistakes
Even experienced artists sometimes encounter issues while working in Substance 3D Stager . Here are a few tips to help you avoid common pitfalls:
- Don’t forget to save your project to avoid losing progress.
Example: “I once lost an hour of work because I forgot to hit Save . Since then, I always save my project every 15–20 minutes.” - If the object looks unnatural, try adjusting material parameters.
Tip: Sometimes even a small tweak to roughness or metallic settings can dramatically improve the appearance of the object. For example, a surface that’s too glossy might look artificial if it’s supposed to be matte. - Check your UV mapping before starting work.
A mistake in UV mapping can lead to stretched or distorted textures. Make sure all parts of the model are properly placed on the UV map. - Don’t overload the scene with details.
Example: “I often add too many objects or effects, and the scene ends up looking overloaded. It’s better to start with minimal elements and gradually enhance them.”
Why You Should Master Substance 3D Stager Right Now
Substance 3D Stager is a powerful tool that opens up endless possibilities for creating realistic scenes. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced professional, this program will become your trusted assistant in the world of 3D graphics.
We’ve covered the key aspects of working with the software:
- How to install and set up your workspace.
- How to import and place objects.
- How to create and adjust materials.
- How to work with lighting and cameras.
- How to export scenes and integrate them into other programs.
Now that you’ve mastered the basics, it’s time to start practicing. Download the trial version of Substance 3D Stager and create your first stage today!




























Leave a Reply